|
To solve the sequence induction problem using random constants, F = {+, -, *},
T = {a, ?}, the set of integer random constants R = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, and “?” ranged over the integers 0, 1, 2, and 3. The parameters used per run are shown in the first column of
Table 2. In this experiment, the first perfect solution was found in generation 45 of run 9 (the sub-ETs are linked by addition):
|
Gene 0: *-aa+-a?aaa??1742174
A0 = {0, 0, 2, 3, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1,
3}
Gene 1: ++*/+-?aaa???4460170
A1 = {3, 0, 2, 2, 1, 3, 1, 0, 0,
1}
Gene 2: *a**++aa?aa??4101213
A2 = {1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 0, 1, 1,
2}
Gene 3: **+--+?aaa???2637797
A3 = {0, 0, 2, 3, 3, 3, 0, 0, 1,
0}
Gene 4: +?*++?aaaa?a?2890192
A4 = {1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 3, 1, 0, 0,
2}
Gene 5: -+-/*-?aa?a?a8147432
A5 = {0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0,
0}
Gene 6: **aa**?aa?a??2314518
A6 = {0, 2, 3, 2, 3, 1, 3, 2, 3,
0}
|
which corresponds to the target sequence (3.2).
As shown in the first column of Table 2, the probability of success for this problem is 16%, considerably lower than the 81% of the second approach (see
Table 2, column 2). It is worth emphasizing that only the prior knowledge of the solution enabled us, in this case, to choose correctly the type and the range of the random constants.
To find the “V” shaped function using random constants F = {+, -, *, /, L, E, K, ~, S, C} (“L” represents the natural logarithm, “E” represents
ex, “K” represents the logarithm of base 10, “~” represents
10x, “S” represents the sine function, and “C” represents the cosine) and
T = {a, ?}. The set of rational random constants R = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, and “?” ranged over the interval [-1, 1]. The parameters used per run are shown in the third column of
Table 2. The best solution, found in run 50 after 4584 generations, is shown below (the sub-ETs are linked by addition):
|
Gene 0: L*L*ECaa??a??8534167
A0 =
{0.189, 0.13, 0.753, 0.548, 0.277, 0.257, 0.743, 0.46, 0.066,
0.801}
Gene 1: ~S/aC-??aa?aa5477773
A1 =
{0.337, 0.99, 0.536, 0.406, 0.283, 0.95, 0.968, 0.108, 0.672,
0.644}
Gene 2: ~*/a*aa???a?a1437777
A2 =
{0.247, 0.929, 0.779, 0.89, 0.926, 0.24, 0.667, 0.254, 0.518,
0.927}
Gene 3: -C*?/*a?aaa??4725239
A3 =
{0.792, 0.019, 0.472, 0.005, 0.682, 0.605, 0.094, 0.357, 0.074,
0.713}
Gene 4: +E+*EE?a?a???4233680
|
|
|
A4 = {0.883, 0.768, 0.899, 0.311, 0.981, 0.845, 0.428, 0.308, 0.519,
0.381} |
(3.4) |
It has a fitness of 1989.566 and an R-square of 0.9997001 evaluated over the set of 20 fitness cases and an R-square of 0.9997185 evaluated against a test set of 100 random points also chosen from the interval [-1, 1]. Mathematically, it corresponds to the following function (the contribution of each sub-ET is indicated in square brackets):
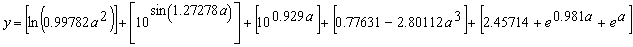
which is a very good approximation to the target function (3.3) as the high value of R-square indicates.
It is worth noticing that the algorithm does in fact integrate constants in the evolved solutions, but the constants are very different from the expected ones. Indeed, GEP (and I believe, all genetic algorithms with tree representations) can find the expected constants with a precision to the third or fourth decimal place when the target functions are simple polynomial functions with rational coefficients and/or when it is possible to guess pretty accurately the function set, otherwise a very creative solution would be found.
To predict sunspots using random numerical constants F = {+, -, *,
/}4 and T = {a, b, c, d,
e, f, g, h, i, j, ?}. The set of rational random constants
R = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, and “?” ranged over the interval [-1, 1]. The parameters used per run are shown in the fifth column of
Table 2. The best solution, found in run 92 after 4759 generations, is shown below (the sub-ETs are linked by addition):
|
Gene 0: /*++j+hjjijg?cfda894833994
A0 =
{0.977, 0.421, 0.226, 0.325, 0.933, 0.204, 0.594, 0.8, 0.212,
0.395}
Gene 1: /++b+*+ag?c?eiejb795620470
A1 =
{0.72, 0.447, 0.266, 0.511, 0.304, 0.247, 0.159, 0.847, 0.204,
0.995}
Gene 2: /*++jj*+jii??f?ig454696802
|
|
|
A2 = {0.52, 0.595, 0.714, 0.982, 0.987, 0.916, 0.153, 0.779, 0.987,
0.672} |
(3.5) |
It has a fitness of 86603.2 and an R-square of 0.833714 evaluated over the set of 90 fitness cases. Mathematically, it corresponds to the following function:
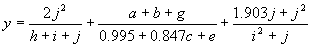
|